一、研究团队概况(Research overview)
巡检机器人研究团队由9名教职工和数十名博士、硕士研究生组成,目前以各种工业巡检任务为应用背景,研究地面轮式巡检机器人和空中旋翼飞行机器人,使之具备目标识别、缺陷检测、动态跟踪等功能。通过携带气体浓度传感器,可以构建流体运动地图,分析烟羽扩散规律,追溯气体泄漏源头。
The inspection robot research team consists of 9 faculty members and dozens of doctoral and master's degree students. Currently, focusing on various industrial inspection tasks, the team is researching ground-wheeled inspection robots and aerial rotorcraft flying robots, so as to equip them with functions such as target recognition, defect detection, and dynamic tracking. By integrating gas concentration sensors, they can construct fluid motion maps, analyze the diffusion patterns of smoke plumes, and trace the sources of gas leaks.
该团队主要研究机器人自主巡检作业的基础理论与工程技术,属于多学科交叉领域,包括机器人定位与构图、规划与导航、智能控制、图像处理、数据融合、目标识别与跟踪、人机交互,以及空中-地面协作巡检等科学问题,尽早发现被检设备可能出现的破损、脱落、过热、过压、泄漏、爆炸、停机等缺陷或异常,从而将用户从繁重而且危险的人工操作中解脱出来,提高测量精度和巡检效率,为维护各类设施安全可靠运行提供重要支撑。
The team mainly researches the basic theory and engineering technology of autonomous robot inspection, which belongs to the interdisciplinary field, including robot positioning and mapping, planning and navigation, intelligent control, image processing, data fusion, target recognition and tracking, human-machine interaction, and aerial-ground collaborative inspection and other scientific issues. The primary goal is to detect potential defects or anomalies in inspected equipment such as damage, detachment, overheating, overpressure, leakage, explosion, or shutdown as early as possible. Therefore, it relieves users from laborious and hazardous manual operations, enhances measurement accuracy and inspection efficiency, and provides crucial support for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of various facilities.
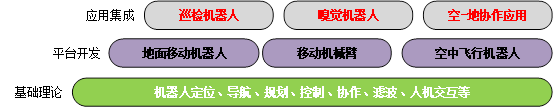
The introduction of inspection robot research team
二、研究团队成员(Faculty members)
(1)团队负责人(Leader)
 吴怀宇,中共党员,工学博士,二级教授,博士生导师。毕业于清华大学。国家教学团队带头人、国家一流专业负责人、国家线下一流课程负责人、国家精品课程负责人、国家精品资源共享课程负责人。兼任教育部本科教学评估专家、中国工程教育专业认证核心专家、电子信息与电气工程类专业认证委员会学术委员会委员、湖北省自动化学会副理事长、湖北省人工智能学会副理事长、美国IEEE高级会员。长期从事自动化及其相关领域的教学与科研工作和高等教育教学管理与研究工作。主持国家和省级教研课题6项,主持国家自然科学基金面上项目3项、湖北省科技支撑计划和企业技术改造课题多项,在 IEEE Trans. on Robotics、IEEE/ASME Trans. on Mechatronics、IEICE Trans. on Electronics, Mechatronics、Neurocomputing、控制理论与应用、电气与电子教学学报等期刊上发表论文100余篇,授权发明专利40余项,出版专著1部,主编教材2部(《自动控制原理》获批“十二五”普通高等教育国家级规划教材),获国家教学成果一等奖、二等奖各1项。【研究生导师链接】
吴怀宇,中共党员,工学博士,二级教授,博士生导师。毕业于清华大学。国家教学团队带头人、国家一流专业负责人、国家线下一流课程负责人、国家精品课程负责人、国家精品资源共享课程负责人。兼任教育部本科教学评估专家、中国工程教育专业认证核心专家、电子信息与电气工程类专业认证委员会学术委员会委员、湖北省自动化学会副理事长、湖北省人工智能学会副理事长、美国IEEE高级会员。长期从事自动化及其相关领域的教学与科研工作和高等教育教学管理与研究工作。主持国家和省级教研课题6项,主持国家自然科学基金面上项目3项、湖北省科技支撑计划和企业技术改造课题多项,在 IEEE Trans. on Robotics、IEEE/ASME Trans. on Mechatronics、IEICE Trans. on Electronics, Mechatronics、Neurocomputing、控制理论与应用、电气与电子教学学报等期刊上发表论文100余篇,授权发明专利40余项,出版专著1部,主编教材2部(《自动控制原理》获批“十二五”普通高等教育国家级规划教材),获国家教学成果一等奖、二等奖各1项。【研究生导师链接】
(2)团队成员(Team members)
 熊凌,女,博士,教授,美国华盛顿州立大学访问学者。毕业于华中科技大学图像识别与人工智能研究所,获工学博生学位。主要研究领域:模式识别与智能系统、图像处理及其应用等。主持完成国家自然科学基金1项,参加国家自然科学基金项目4项,主持湖北省自然科学基金1项、湖北省技术创新专项重点项目2项、湖北省重点研发项目1项。获湖北省科技进步二等奖2项、湖北省技术发明三等奖1项、中国机械工业科学技术进步二等奖1项;获授权发明专利和实用新型专利10余项、软件著作权3项;发表学术论文50余篇。主编或副主编教材5部,获国家级教学成果二等奖1项、省级教学成果二等奖1项。【研究生导师链接】
熊凌,女,博士,教授,美国华盛顿州立大学访问学者。毕业于华中科技大学图像识别与人工智能研究所,获工学博生学位。主要研究领域:模式识别与智能系统、图像处理及其应用等。主持完成国家自然科学基金1项,参加国家自然科学基金项目4项,主持湖北省自然科学基金1项、湖北省技术创新专项重点项目2项、湖北省重点研发项目1项。获湖北省科技进步二等奖2项、湖北省技术发明三等奖1项、中国机械工业科学技术进步二等奖1项;获授权发明专利和实用新型专利10余项、软件著作权3项;发表学术论文50余篇。主编或副主编教材5部,获国家级教学成果二等奖1项、省级教学成果二等奖1项。【研究生导师链接】
 程磊,男,博士,教授,英国西英格兰大学联合博士生导师。入选“湖北省新世纪高层次人才工程”计划,第九届武汉市“洪山地区十大优秀青年”。长期从事机器人与智能嗅视感知等方面的研究与教学工作。兼任中国人工智能学会青年工作委员会常务委员、中国人工智能学会智能机器人专业委员会常务委员、湖北省自动化学会理事、湖北省人工智能学会理事、武汉市自动化学会常务理事。主持及参与国家自然科学基金6项,主持省部级科教研项目9项,发表论文60余篇,获国际国内学术奖励10项、学生竞赛国家奖20余项。【研究生导师链接】
程磊,男,博士,教授,英国西英格兰大学联合博士生导师。入选“湖北省新世纪高层次人才工程”计划,第九届武汉市“洪山地区十大优秀青年”。长期从事机器人与智能嗅视感知等方面的研究与教学工作。兼任中国人工智能学会青年工作委员会常务委员、中国人工智能学会智能机器人专业委员会常务委员、湖北省自动化学会理事、湖北省人工智能学会理事、武汉市自动化学会常务理事。主持及参与国家自然科学基金6项,主持省部级科教研项目9项,发表论文60余篇,获国际国内学术奖励10项、学生竞赛国家奖20余项。【研究生导师链接】
 陈洋,男,教授,博士生导师,国家公派新加坡南洋理工大学访问学者。毕业于中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所机器人学国家重点实验室,获工学博士学位。湖北省自动化学会理事,湖北省人工智能学会理事,中国自动化学会机器人竞赛工作委员会委员。主要研究领域为移动机器人建模、规划与控制。主持国家自然科学基金项目3项、国家重点研发计划专项子课题1项、辽宁省科技厅联合基金1项、湖北省教育厅科研课题1项。发表学术论文50多篇,发明专利10项(包括美国发明专利1项),实用新型专利2项,软件著作权登记5项。获得省级教学成果二等奖1项,被评为首届武汉科技大学优秀研究生导师。【研究生导师链接】
陈洋,男,教授,博士生导师,国家公派新加坡南洋理工大学访问学者。毕业于中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所机器人学国家重点实验室,获工学博士学位。湖北省自动化学会理事,湖北省人工智能学会理事,中国自动化学会机器人竞赛工作委员会委员。主要研究领域为移动机器人建模、规划与控制。主持国家自然科学基金项目3项、国家重点研发计划专项子课题1项、辽宁省科技厅联合基金1项、湖北省教育厅科研课题1项。发表学术论文50多篇,发明专利10项(包括美国发明专利1项),实用新型专利2项,软件著作权登记5项。获得省级教学成果二等奖1项,被评为首届武汉科技大学优秀研究生导师。【研究生导师链接】
 陈琳,女,博士,讲师。2006年毕业于华中科技大学获工学硕士学位。2018年毕业于武汉大学系统工程研究所,获得博士学位,主要研究领域:控制理论,博弈论,合作博弈。参与国家自然科学基金项目3项,获得国家级教学成果二等奖1项、省级教学成果二等奖1项,参与编写教材2部,曾获武汉科技大学讲课比赛一等奖。主持教研项目2项,发表教研论文多篇。
陈琳,女,博士,讲师。2006年毕业于华中科技大学获工学硕士学位。2018年毕业于武汉大学系统工程研究所,获得博士学位,主要研究领域:控制理论,博弈论,合作博弈。参与国家自然科学基金项目3项,获得国家级教学成果二等奖1项、省级教学成果二等奖1项,参与编写教材2部,曾获武汉科技大学讲课比赛一等奖。主持教研项目2项,发表教研论文多篇。
 郑秀娟,女,博士,副教授。2016年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。主要研究方向为机电/能源系统状态评估、退化建模与寿命预测,信息物理系统的状态估计、滤波、故障诊断与容错控制。主持湖北省自然科学基金面上项目1项,主持完成湖北省自然科学基金青年项目1项,湖北省教育厅科学技术研究重点项目1项。在Energy、Reliability Engineering & System Safety、International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control、控制与决策、控制理论与应用等学术期刊和国际会议上发表SCI/EI收录论文20余篇,获得授权发明专利和实用新型专利2项。【研究生导师链接】
郑秀娟,女,博士,副教授。2016年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。主要研究方向为机电/能源系统状态评估、退化建模与寿命预测,信息物理系统的状态估计、滤波、故障诊断与容错控制。主持湖北省自然科学基金面上项目1项,主持完成湖北省自然科学基金青年项目1项,湖北省教育厅科学技术研究重点项目1项。在Energy、Reliability Engineering & System Safety、International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control、控制与决策、控制理论与应用等学术期刊和国际会议上发表SCI/EI收录论文20余篇,获得授权发明专利和实用新型专利2项。【研究生导师链接】
 陈志环,2017年博士毕业于华中科技大学,武汉科技大学副教授,湖北省“楚天学子”,全国“香江学者计划”入选者。2015年10月至2016年10月期间获国家留学基金委资助公派西澳大利亚大学联合培养。2021年1月到2023年1月受国家博士后基金委和香港香江学者学会资助公派香港城市大学访问研究,主要研究方向:复杂系统的观测器和控制器设计、分数阶微积分、非线性动力学(混沌)、机器人路径规划和多目标优化算法等。在Energy、ISA transaction、IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers等期刊以第一/通讯作者发表SCI论文30余篇,其中高被引论文4篇,担任Applied Soft Computing、Expert System with Application、the Journal of Franklin Institute等期刊的审稿人。近些年来,主持过国家自然科学基金(青年项目)、博士后面上基金、湖北省自然科学基金等项目,参与过国家自然科学基金(面上项目)2项。【研究生导师链接】
陈志环,2017年博士毕业于华中科技大学,武汉科技大学副教授,湖北省“楚天学子”,全国“香江学者计划”入选者。2015年10月至2016年10月期间获国家留学基金委资助公派西澳大利亚大学联合培养。2021年1月到2023年1月受国家博士后基金委和香港香江学者学会资助公派香港城市大学访问研究,主要研究方向:复杂系统的观测器和控制器设计、分数阶微积分、非线性动力学(混沌)、机器人路径规划和多目标优化算法等。在Energy、ISA transaction、IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers等期刊以第一/通讯作者发表SCI论文30余篇,其中高被引论文4篇,担任Applied Soft Computing、Expert System with Application、the Journal of Franklin Institute等期刊的审稿人。近些年来,主持过国家自然科学基金(青年项目)、博士后面上基金、湖北省自然科学基金等项目,参与过国家自然科学基金(面上项目)2项。【研究生导师链接】
 胡棉,女,博士,讲师。2020年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。主要研究方向为智能电网及能源互联网的能源管理与优化调度。以第一作者在IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics、Energy、International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems国际期刊上发表SCI收录论文3篇,获授权中国发明专利4项。主持国家自然科学基金青年项目1项、湖北省自然科学基金青年项目1项,参与国家级和省部级自然科学基金项目5项、国家电网公司总部科技项目1项,获得省级教学成果二等奖1项。【研究生导师链接】
胡棉,女,博士,讲师。2020年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。主要研究方向为智能电网及能源互联网的能源管理与优化调度。以第一作者在IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics、Energy、International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems国际期刊上发表SCI收录论文3篇,获授权中国发明专利4项。主持国家自然科学基金青年项目1项、湖北省自然科学基金青年项目1项,参与国家级和省部级自然科学基金项目5项、国家电网公司总部科技项目1项,获得省级教学成果二等奖1项。【研究生导师链接】
 朱振华,男,博士后。2021年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。研究方向包括奇异系统、多智能体系统分布式协同控制、分布式估计、有限时间控制等。以第一作者或通讯作者在IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers、IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering、International Journal of Control等国际权威期刊上发表SCI论文6篇。作为研究骨干,参与国家自然科学基金重点项目1项和国家自然科学基金面上项目2项。
朱振华,男,博士后。2021年毕业于华中科技大学控制科学与工程专业,获工学博士学位。研究方向包括奇异系统、多智能体系统分布式协同控制、分布式估计、有限时间控制等。以第一作者或通讯作者在IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers、IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering、International Journal of Control等国际权威期刊上发表SCI论文6篇。作为研究骨干,参与国家自然科学基金重点项目1项和国家自然科学基金面上项目2项。
三、研究方向(Research interests)
(1)变电站巡检机器人
研究领域:
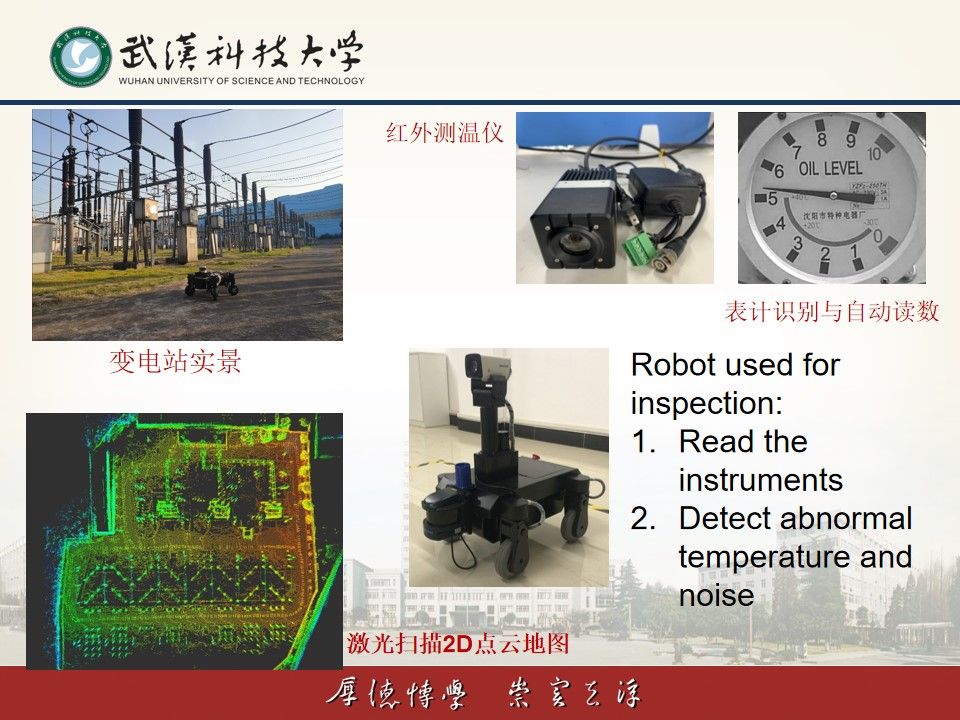
传统的人工作业方式对变电站设施进行巡检具有危险性高、劳动强度大等问题。该研究方向以室外变电站为典型应用环境,研究和开发无人值守巡检机器人。机器人可以自动构建地图和自主导航,可实现自主检测、自动读表、异常报警等功能。所有巡检数据无线传输到控制室,在后台提供调阅和分析功能,极大地提高了巡检效率。
(1) Substation Inspection Robot
Research Field:
Traditional manual methods of inspecting substation facilities are associated with high risks and heavy labor intensity. This research focuses on outdoor substations, aiming to develop unmanned inspection robots. These robots are capable of autonomously constructing maps and navigating, enabling autonomous detection, automatic meter reading, anomaly detection, and other functions. All inspection data is wirelessly transmitted to the control room, where backend access and analysis capabilities are provided, greatly enhancing inspection efficiency.
研究内容:
变电站巡检机器人的研究主要包括全向地面移动平台、双机械臂协调控制、基于多感知系统的巡检维护与遥操作等,其中以基于多感知系统的巡检维护与遥操作为主要研究内容。
Research Content:
The research on substation inspection robots mainly includes omnidirectional ground mobile platforms, coordinated control of dual manipulator arms, inspection and maintenance based on multi-sensory systems, and remote operation. The main research content is the inspection and maintenance based on multi-sensory systems.
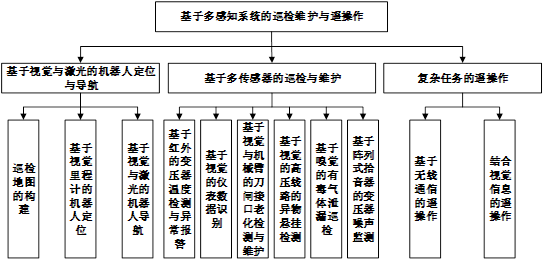
图1 变电站巡检机器人研究内容

图2 变电站巡检机器人样机
运输机器人
技术方法:
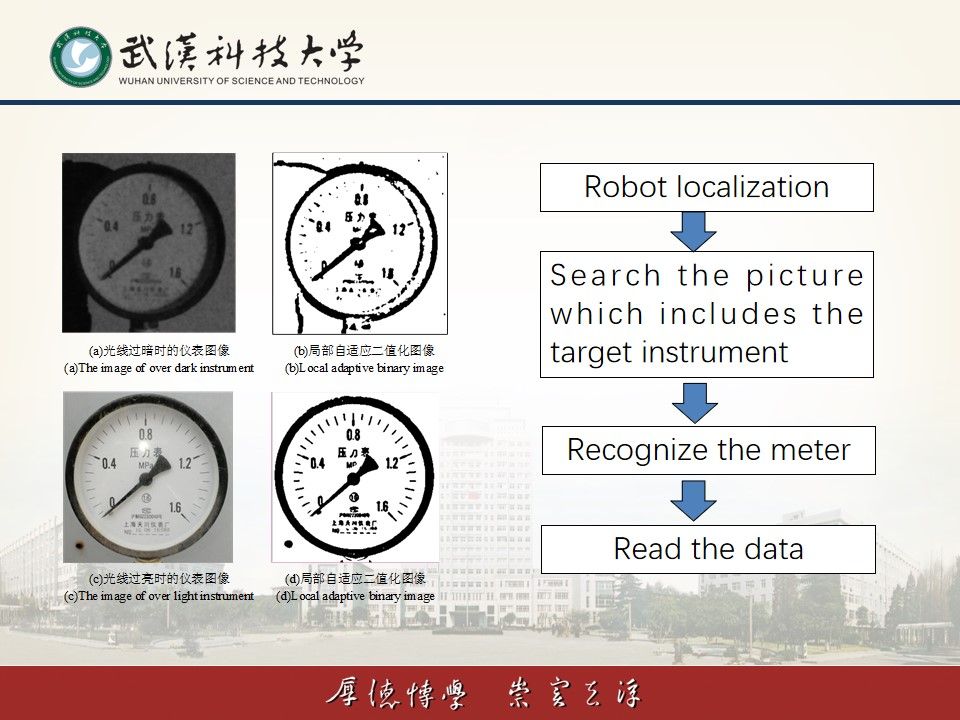
1)变电站巡检机器人基于机器视觉和激光传感器进行自定位,实现自主导航。
2)变电站巡检机器人可以自主识别仪表并进行读数,实时发现异常气味并对放射源定位、提取运行设备声音分析故障状况、实时获取测温点数据并对异常进行报警等。
3)变电站巡检机器人借助双机械臂实现简单维护功能,具有手动遥操作和自主控制两种模式,如打开和关闭控制柜、打开和切断开关、清除简单路障等。
Technical methods:
1) The substation inspection robot uses machine vision and laser sensors for self-localization and autonomous navigation.
2) The substation inspection robot can autonomously identify instruments and read their readings, detect abnormal odors in real-time, locate radioactive sources, extract sound for equipment fault analysis, obtain temperature data from measurement points in real-time, and issue alerts for anomalies.
3) The substation inspection robot employs dual robotic arms for basic maintenance tasks. It features two modes: manual remote operation and autonomous control. Tasks include opening and closing control cabinets, operating switches, and clearing simple obstacles.
(2)飞行机器人
研究领域:
近年来,以微型无人机为代表的飞行机器人因具有体积小、成本低、适应性强等特点而成为了国内外研究热点,并逐渐在军事、民用等诸多领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。目前本研究团队主要以旋翼无人机为对象,研究先进的控制理论和相关的应用问题,涉及无人机的导航、定位、规划、控制等方面。研究团队在此领域有十多年的积累,先后开发了多款飞行控制系统。
(2) Flying Robot
Research Field:
In recent years, flying robots, particularly micro UAVs, have emerged as a prominent focus in research, both domestically and internationally. These robots are characterized by small size, low cost, and high adaptability, leading to significant potential applications across various fields, including military and civilian sectors. Our research team primarily concentrates on rotary-wing UAVs, delving into advanced control theories and associated application issues such as navigation, localization, planning, and control.
研究内容:
飞行机器人的研究主要包括路径规划、动力学建模、控制器设计、位姿解算以及状态反馈等,其中以动力学建模、控制器设计以及状态反馈为主要研究内容。
Research Content:
The research of flying robots mainly includes path planning, dynamics modeling, controller design, attitude solving, and state feedback, among which dynamics modeling, controller design, and state feedback are the main research contents.

图3 研究内容

图4 四旋翼无人机
未来飞行器
技术方法:
1)以图4所示四旋翼无人机为例,根据牛顿运动定律和欧拉方程,可建立四旋翼无人机的动力学模型方程。
2)根据环境特点和任务要求设计控制器。本团队曾开发的控制算法有PID、Backstepping、滑模控制、LQR、反馈线性化、模糊PID控制等。
3)实际应用中传感器采集到的飞行状态信息存在噪声,需要状态信息进行滤波甚至补偿。本团队曾开发的滤波方法有互补滤波、梯度下降法、卡尔曼滤波等。
Technical methods:
1) Taking the quadrotor UAV illustrated in Fig. 4 as an example, according to Newton's laws of motion and Euler's equations, the dynamic model of the quadrotor UAV can be established.
2) Designing controllers tailored to environmental characteristics and mission requirements constitutes a crucial aspect of our research. Our team has developed various control algorithms, including PID, Backstepping, sliding mode control, LQR, feedback linearization, and fuzzy PID control, to address diverse control challenges effectively.
3) In practical applications, sensor-derived flight status information often suffers from noise, necessitating the use of filtering or compensation techniques. Our team has developed several filtering methods, such as complementary filtering, gradient descent method, and Kalman filtering, to enhance the accuracy and reliability of flight state estimation.
(3)嗅觉机器人
研究领域:
现代感知技术的进步推动了机器人向立体空间发展和应用,该研究方向结合旋翼无人机、足式机器人等特种机器人,将机器人应用于当前国计民生重点关注的环境问题。针对三维大气环境,研制具有空中嗅觉的气体分布动态监测自主机器人系统;针对水域环境,研制搭载具有水质监测功能的电子舌无人机;针对小区域环境,研制具有嗅觉溯源功能的足式自主机器人系统。
(3) Olfactory Robot
Research Field:Advancements in modern perception technology have propelled the development and application of robots in three-dimensional space. This research field integrates specialized robots such as rotary-wing UAVs and legged robots to address environmental issues of national concern. For the three-dimensional atmospheric environment, we develop autonomous robot systems capable of dynamically monitoring gas distribution with aerial olfaction. For aquatic environments, we design unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with electronic tongue sensors for water quality monitoring. For localized environments, we develop legged autonomous robot systems with odor tracing capabilities.
气体监测:
该研究方向借助多旋翼无人机,对三维空间的气体浓度分布进行动态构图,并探索气味源追溯方法。先分配待测空间区域,规划好旋翼机器人的飞行路径,然后根据传感器采集到的浓度进行子地图构建,进而将多个子地图融合成一幅完整地图,最后实现气味源定位。
Gas Monitoring:
This research direction utilizes multi-rotor UAVs to dynamically map the distribution of gas concentrations in three-dimensional space and explore methods for tracking odor sources. The process involves allocating the space to be measured, planning the flight paths of the rotary-wing robots, constructing sub-maps based on sensor-collected concentrations, merging multiple sub-maps into a complete map, and finally, locating the odor source.

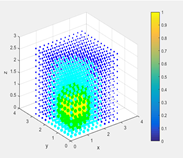
(a)气体检测无人机 (b)气体浓度分布图
图5 气体监测
水域监测:
该研究方向研制具备水质检测功能的电子舌传感器,重点对水域亚硝酸盐含量、氨氮含量、PH值、溶氧量等进行检测,借助多旋翼无人机,对江河、湖泊等水域环境的水质分布进行动态监测,并分析预测水域水质变化。
Water Monitoring:
This research direction focuses on developing electronic tongue sensors capable of detecting water quality parameters such as nitrite content, ammonia nitrogen content, pH value, and dissolved oxygen content. Utilizing multi-rotor UAVs, we dynamically monitor the distribution of water quality in river and lake environments and analyze and predict changes in water quality.


(a)水域监测无人机 (b)电子舌传感器
图6 水域监测
水质监测机器人
足式嗅觉机器人:
该研究方向借助六足机器人,对小区域环境的气味源进行搜索定位。探索六足机器人运动学及其控制算法,并集成各类气体传感器进行气味源自主搜索、路径规划、避障、定位研究等。
Legged Olfactory Robots:
This research direction utilizes hexapod robots to search for and locate odor sources in localized environments. It explores hexapod robot kinematics and control algorithms and integrates various gas sensors for autonomous odor source search, path planning, obstacle avoidance, and localization research.


(a)六足机器人 (b)气体寻源
图7 足式嗅觉机器人
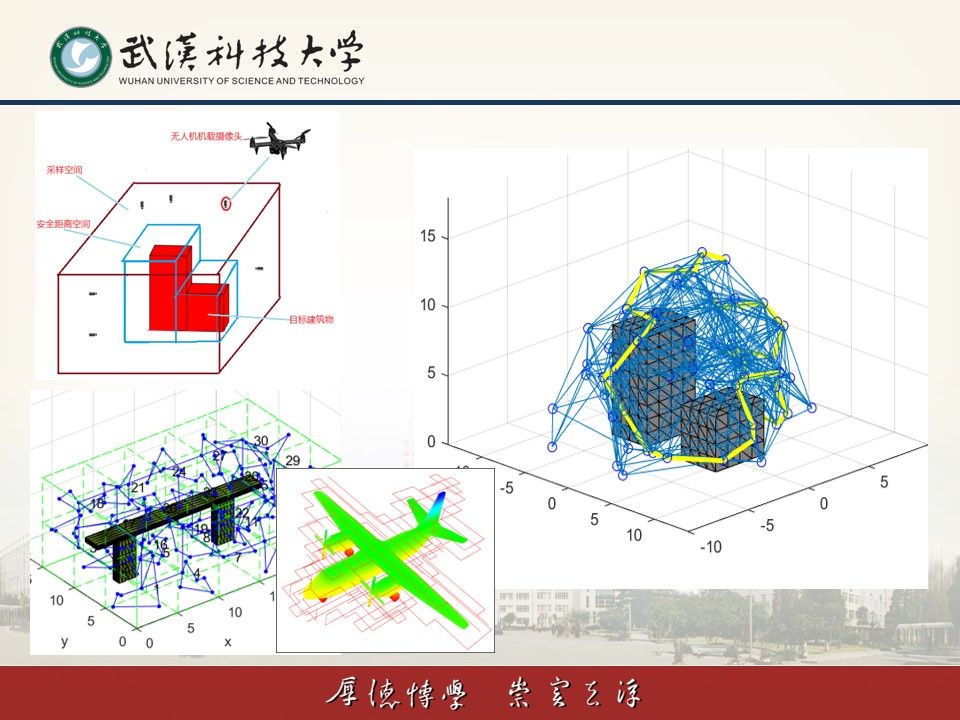
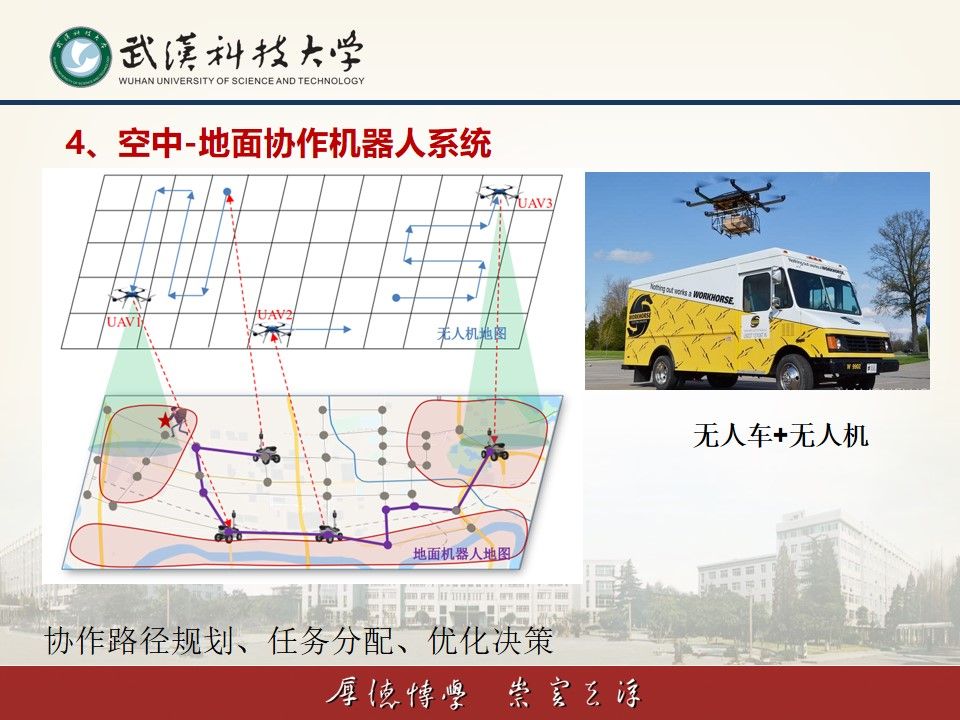
(4)空中-地面多机器人协作系统
将空中无人机与地面移动机器人结合构成异构协作系统,可以充分发挥两类系统各自的优势。比如,微型无人机运动灵活、视野开阔,在搜索和监测目标方面具有不可取代的优势,但是无人机单次续航时间通常有限。地面机器人具有载荷多、航程大的特点,正好可以充当空中无人机的着陆平台和移动补给站,但是地面机器人只能在给定的道路网络中运动,其巡检范围和视角严重受限。因此,将这两类机器人集成在一起协同作业,可以取长补短、优势互补,可以大大拓展机器人系统的巡检能力。该方向主要研究这一类异构系统的协作路径规划、任务分配、资源调度等科学问题,研究成果在无人机快递、生物监测与保护、边境巡逻等领域具有广泛的应用前景。
(4) Air-Ground Multi-Robot Collaboration System
Combining aerial drones with ground mobile robots forms a heterogeneous collaborative system, which can fully leverage the advantages of both types of systems. For instance, micro UAVs are agile and have a broad field of view, making them irreplaceable in target search and monitoring. However, UAVs typically have limited endurance for single missions. Ground robots, on the other hand, have the advantage of carrying heavier payloads and traveling longer distances. They can serve as landing platforms and mobile supply stations for UAVs. However, ground robots are confined to predefined road networks, severely limiting their inspection range and perspective. Therefore, integrating these two types of robots to work together can complement each other's strengths and weaknesses, significantly expanding the inspection capabilities of robot systems. This research direction mainly focuses on scientific issues such as collaborative path planning, task allocation, and resource scheduling for such heterogeneous systems. The research outcomes have broad applications in fields such as UAV delivery, biodiversity monitoring and protection, border patrol.
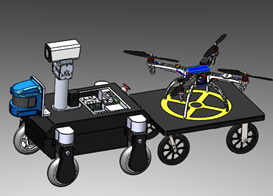

图8 空中-地面多机器人协作系统
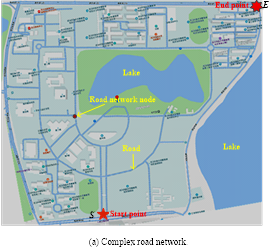
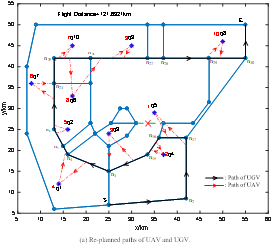
图9 UAV-UGV协作路径规划
空地异构机器人
四、科研条件(Office and Equipment)


图10 办公地点(武汉科技大学青山校区钢铁楼1201~1208、1304)

图11 变电站巡检机器人实验室1201

图12 建筑物巡检机器人实验室1204








五、近几年主持科研项目(Projects)
[1] 国家自然科学基金:受扰合作竞争多智能体系统的预设时间协调控制研究(62303360),2024-2026
[2] 国家自然科学基金:面向海岛微电网的多能互补分布式优化调度研究(62203339),2023-2025
[3] 国家自然科学基金:面向空-地协作持续监测的多机器人路径规划研究(62173262),2022-2025
[4] 国家自然科学基金:共融环境中巡逻机器人协作模式及优化方法研究(62073250),2021-2024
[5] 国家自然科学基金:水轮发电机组网络的分数阶建模与同步控制研究(62003249),2021-2023
[6] 国家自然科学基金:面向大型储罐立体巡检的四旋翼无人机自主控制方法研究(61703314),2018-2020
[7] 国家自然科学基金:面向动态任务合作的空地异构多机器人自主规划研究(61573263), 2016-2019
[8] 国家自然科学基金:基于灵长目动物视觉认知原理的旋翼无人机自主规划方法研究(61203331), 2013-2015
[9] 国家自然科学基金:基于地形正演的全张量重力梯度水下辅助导航方法研究. (61104191),2012-2014
[10] 国家自然科学基金:全区域覆盖可拓展模块化移动机械臂控制系统研究(61075087),2011-2013
[11] 国家自然科学基金:基于图论分析的多移动机器人有序化多模态群集运动控制(60705035),2008-2010
[12] 国家自然科学基金:低雷诺数气动特性与微机电系统控制的多学科优化设计研究(50675161),2007-2009
[13] 湖北省科技支撑计划(研发与示范类):变电站巡检维护一体化机器人系统研发(2015BAA018),2015-2017
[14] 湖北省自然科学基金:面向动态通信拓扑的信息物理融合系统安全状态估计,2023AFB619,2024-2025
[15] 湖北省自然科学基金:面向多能源互联的区域综合能源系统协同优化运行技术研究,(2022CFB602),2022-2024
[16] 湖北省自然科学基金:复杂闭环控制系统的故障诊断方法及在无人机中的应用(2018CFB375),2018-2019
[17] 湖北省自然科学基金:基于语音伺服的全区域覆盖轮式服务机器人(2010CDA005),2011-2012
[18] 中国博士后科学基金:水轮机调节系统的智能分数阶滑模控制(2018M632932),2018-2020
[19] 国家重点研发计划专项子课题“人机协同的目标跟踪与主动防控技术”(2017YFC0806503-05), 2017.7-2020.12
六、研究生培养(Students)
培养理念:全面提升研究生综合能力
培养目标:理论水平和技术能力达到或超过国内985高校毕业生水平
在读博士生:
祝彦成、孙艳琴、齐卉、华铁丹、徐梦飞、王泓力
在读硕士生:
2023级(18人):李 轲、赵 威、龚秒洲、 胡 颖 、柳青、 刘 城 、俞 锴、余慧慧、黄太子、崔辰宇、Ametepee Nehemia Kwame Mensah、晏希文、贺相凯、王德文、王思宇、袁子依、易 旭、范芝仪
2022级(33人):吴艳晖、彭 超、安彦波、钟贤能、李洁洁、邬 吉、王 荣、罗继成、张 雨、姚天晓、陶 翔、Essel Emmanuel、孙梓滢、柳云飞、田 亮、李旭东、钟佳龙、邹克勤、Yalley Abraham Kojo、丁 昕、梁东风、李 威、程占波、郭 龙、陈志恒、施廷浩、席诗雨、刘 钰、李晓霞、魏 杰、刘文博、陈少华、杨 燕
2021级(28人):仇玉宜、孟 彪、陶流俊、陈 帆、张 锬、张得才、王好友、王文乐、汤戴维、谭超强、侯兵兵、李凤云、秦孝林、段 贺、王霄龙、周 锐、钟树成、李胜昔、刘午虓、詹欣茹、陈琳国、代啟亮、胡佳辉、李长君、梁成龙、戴雪刚、王祖傲、胡 映
七、优秀毕业生(Former graduates)
表1 湖北省优秀硕士论文获得者
年份
| 论文题目
| 研究生姓名
| 研究生专业
|
2016
| 物联网模式下机器人室内复合定位系统研究
| 周明达 | 控制理论与控制工程
|
2013
| 移动机械臂的运动控制与轨迹规划算法研究 | 郑秀娟
| 控制理论与控制工程 |
2009
| 基于激光测距仪的同步定位与建图研究
| 赵 季
| 控制理论与控制工程 |
表2 武汉科技大学校长奖章获得者
获奖年份
| 研究生姓名
| 研究生专业 | 获奖比例 |
2019
| 梅壮
| 控制科学与工程
| 1/10
|
表3 国家奖学金获得者
| 获奖年份 | 研究生姓名
| 研究生专业
| 学历层次 |
2020
| 刘家乐
| 控制工程 | 硕士 |
2019
| 严雷
| 控制工程 | 硕士 |
| 赵熙桐 | 控制工程 | 硕士 |
2018
| 张思伦
| 控制科学与工程 | 硕士 |
| 彭锐 | 控制科学与工程 | 硕士 |
梅壮
| 控制科学与工程 | 硕士 |
任诗文
| 控制科学与工程 | 硕士 |
2017
| 刘友才
| 控制科学与工程 | 硕士 |
龙文
| 控制工程 | 硕士 |
2016
| 张德龙
| 电路与系统
| 硕士 |
表4 优秀毕业生
毕业年份
| 研究生姓名
| 研究生专业
| 获奖比例
|
2021
| 胡子峰 | 控制工程 | 3/13
|
李琳
| 控制工程 |
| 路浩 | 控制工程 |
2020
| 刘钦 | 控制科学与工程 | 5/13
|
严雷
| 控制工程 |
| 姚栋 | 控制工程 |
| 张巩 | 控制工程 |
| 赵熙桐 | 控制工程 |
2019
| 彭锐 | 控制科学与工程 | 3/10
|
梅壮
| 控制科学与工程 |
| 任诗文 | 控制科学与工程 |
2018
| 代雅婷
| 控制科学与工程 | 1/10
|
更新日期:2024年3月5日
更新信息可见网址:https://www.labxing.com/-10334
